What Is Periodontitis and How to Treat It?
According to the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention), 47.2% of adult Americans aged 30 years and above are suffering from periodontal disease. This percentage further rises with age and reaches 70.1% in the case of people aged 65 or above. When it comes to gender differences periodontitis is more common in men (56.4%) as compared to women (38.4%).
You might be astonished by the facts and wondering what periodontitis is, how can I know I have it, what are its possible treatments, and so on?
Well, let us dig deeper to find answers.
What is Periodontitis?
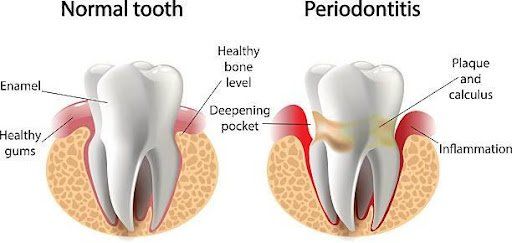
Periodontitis is a gum disease that damages the soft tissue and bone supporting the tooth. This causes loosening of the teeth. In severe cases, the teeth fall out. This disease is common among adults and is seen as one of the major threats to dental health.
Causes
Mouth bacteria is mainly responsible for periodontitis. If not removed properly it starts infecting the tissue that surrounds your tooth. This results in inflammation thus leading to severe conditions.
When you allow bacteria to remain on your tooth for a long time, it forms plaque (a form of a film). This plaque takes the form of tartar with time. The tartar spreads below the gum line and results in Gingivitis. If left untreated it leads to a more serious condition, Periodontitis.
Signs & Symptoms
- Bleeding gums
- Swollen, tender, or red gums
- Receding gums
- Loose teeth
- Pus between gums and teeth
- Bad breath
- Painful chewing
- Sensitive teeth
- The gap between gums and teeth
Treatment
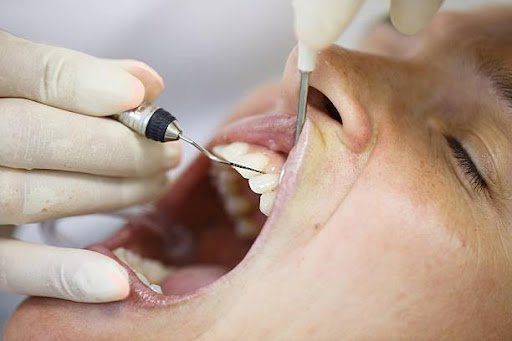
Periodontitis is a severe condition that demands a visit to your dentist. We recommend seeing a trusted oral surgeon in Brooklyn for treatment if you notice any of the symptoms mentioned above.
There are two types of treatments
- Nonsurgical Treatments
- Surgical Treatments
Nonsurgical Treatments
This treatment is preferred when periodontitis is in the beginning phase.
- Scaling: Scaling refers to the removal of tartar and bacteria from the tooth surfaces and beneath the gums. This operation is performed using a special instrument, laser, or ultrasonic device.
- Antibiotics: Oral or Topical antibiotics are used for controlling the bacterial infection. Topical antibiotics include mouth rinse, gel, etc. Oral antibiotics are available in the form of capsules or tablets.
- Root Planning: This smooths the root surfaces and removes plaque and tartar that can aid in developing the disease.
Surgical Treatments
This procedure is adopted when the condition becomes severe.
- Bone Grafting: When periodontitis destroys the bone surrounding the tooth root, oral surgeons go with Bone Grafting. The grafts used in this procedure are composed of small fragments of your bone or they can be synthetic or donated. This procedure holds the tooth in place and serves as a platform for the natural regrowth of bone.
- Flap Surgery: Flap surgery or pocket reduction surgery involves lifting back of a section of gum tissue. This is performed by making tiny incisions in your gum. The surgery will expose the roots thus creating conditions for more effective scaling and root planning.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This surgery is performed to allow the regrowth of a destroyed bone. A special biocompatible fabric is placed between the bone and tooth. This fabric prevents the entry of unwanted tissue into the healing area.
- Tissue-stimulating Proteins: A special gel is applied to the diseased tooth roots. The proteins present in the gel stimulate the growth of healthy tissue and bone.
- Soft Tissue Grafting: This is done for the reinforcement of damaged soft tissue. It prevents gum recession and provides covering to exposed roots.
You must now have a clear understanding of periodontitis. We recommended good oral hygiene to avoid periodontitis. Still, if you notice any signs pay a visit to your oral surgeon in Brooklyn.